Key points on nutritional management of type 2 diabetes
- a healthy diet gives your child the best building blocks to grow, develop and feel well
- good diabetes management is about a balance between healthy eating, physical activity and diabetes medicine
- your child's diabetes team can give you advice that's right for your child

A plate showing suggested portions of food for a healthy balanced meal. Aim for half a plate of non-starchy colour vegetables, quarter of a plate of protein and quarter of a plate of carbohydrates.
Source: KidsHealth
General guidelines on the nutritional management of type 2 diabetes
There are some special considerations needed around food for tamariki and rangatahi with type 2 diabetes, depending on their medicines. Considerations include:
- meal and snack times
- food choices
- portion sizes
Your dietitian can give you more details and advice that's right for your child or young person.
Meals
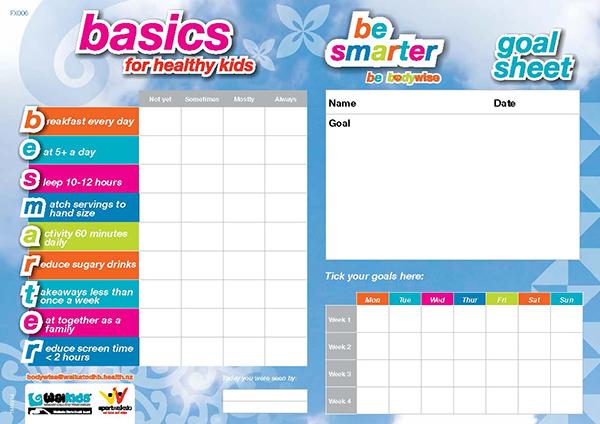
Enjoy 3 meals each day, spread evenly across the day.
Eat together as a whānau (family) as often as possible.
Make meals ‘distraction free’ by taking a break from devices and other activities at mealtimes. Try to reduce the use of electronic media in the evening
Healthy foods from the 4 main food groups
Choose a variety of healthy foods from the 4 main food groups for growth and development. These food groups are:
- fruits and vegetables
- dairy products
- whole grain breads and cereals
- lean meats and alternatives (such as legumes)
Enjoy 2 servings of fruit and at least 5 servings of vegetables each day.
Aim to include some high-fibre (wholegrain) carbohydrate foods at each meal. These foods have a low glycaemic index (GI) and the carbohydrate is digested slowly which is good for blood glucose control.
Limit intake of high fat (especially saturated fat) food
Choose low or reduced-fat dairy products and cheeses.
Choose lean cuts of meat (removing visible fat from meat and skin from chicken and poultry).
Limit high-fat snacks and takeaways, and processed meat.
Eat healthy snacks
Your child can eat a small healthy carbohydrate-based snack in between meals.
Everyday foods and sometimes foods (for special occasions)
Remember 'treats' are not the same as 'snacks'.
Keep foods that are high in fat, sugar and salt for special occasions only. It’s best not to offer these foods as regular snacks. Eating these 'treat' foods regularly may lead to weight gain and increased blood sugar levels etc. Examples of 'treat' foods you might offer on special occasions include potato chips, corn snacks, muesli bars, chocolate, sweets, cakes, sweet biscuits, pies and pastries.
Avoid high sugar drinks such as cordial, powdered drinks, soft drinks and fruit juice (unless using to treat hypoglycaemia).
Treatment for type 2 diabetes
Stabilise blood glucose
The treatment goal for type 2 diabetes is to stabilise blood glucose as much as possible.
Consider food choices
Once your child or young person achieves target blood glucose levels, you may also need to consider food choices that can help to:
- lower blood pressure
- reduce high blood lipids (or cholesterol levels) if needed
Achieve and maintain a healthy weight
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is an important part of diabetes management. It helps prevent health problems later in life.
Make healthy lifestyle changes
It is very important to involve all the whānau in supporting your child or young person to make healthy lifestyle changes.
They can do this by:
- eating a healthy diet centred on whole foods and less processed foods where possible
- being active and doing regular physical activities
- continuing to live a healthy lifestyle throughout their teens and into adulthood
The main parts of good diabetes management
Good diabetes management is about a balance between:
- Healthy eating
- Physical activity
- Diabetes medicine
Sleep
Getting plenty of sleep helps with weight management, feeling good and learning.
Aim for consistent bed and wake-up times and make sure tamariki and rangatahi get enough good quality sleep.
Physical activity
All rangatahi should aim to get 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous activity every day. This should include muscle-strengthening exercises 3 days a week.
Encouraging Children & Young People With Diabetes To Be Active
If your child is using insulin, they may need to do the following around activity, to avoid hypoglycaemia:
- have extra carbohydrate
- adjust insulin dosing
Your diabetes team will discuss this with you.
Aim to limit recreational screen time to a maximum of 2 hours a day. Avoid things that involve sitting for long periods of time.
Please talk with your diabetes team about specific recommendation for your child.
Resources on physical wellbeing for children