Dr Owen Sinclair answers your immunisation questions. Video by Te Whatu Ora
Key points about immunisation
- immunisation protects tamariki against a range of serious diseases
- immunisation on time is the most effective way to protect hapū māmā, pēpi and tamariki from preventable disease
- immunising pēpi the day they turn 6 weeks old is the best way to protect them
- childhood immunisations are free in Aotearoa
- the benefits of immunisation far outweigh the risks
Why your child needs immunisation
Immunising tamariki in Aotearoa against a range of diseases keeps them safe. These diseases can cause serious illness, cancers later in life, and sometimes death.
In the past, diseases such as diphtheria, tetanus and whooping cough killed many tamariki. Today, vaccines protect aganist these and other diseases.
Immunisation has wiped out some of the killer diseases of childhood in New Zealand.
- tetanus is very rare - although it still happens in children who haven't been immunised
- New Zealand is free of polio and diphtheria
But, these diseases still exist in other countries.
Protecting those who can't have immunisations
Immunisation protects your child but it also protects those most at risk. This includes pēpi who are too young for immunisation or tamariki with weakened immune systems. These pēpi and tamariki rely on those around them being immunised.
Epidemics in Aotearoa New Zealand
There are still epidemics or outbreaks of some diseases in Aotearoa, including:
- whooping cough (pertussis)
- measles
- mumps
Where to go for immunisation
You usually need to take pēpi and tamariki to a GP practice for their immunisation.
Some pēpi and tamariki can have their immunisation from other services like Māori and Pacific providers or outreach services.
Immunisation providers in your region at Healthpoint
Immunisations and timings
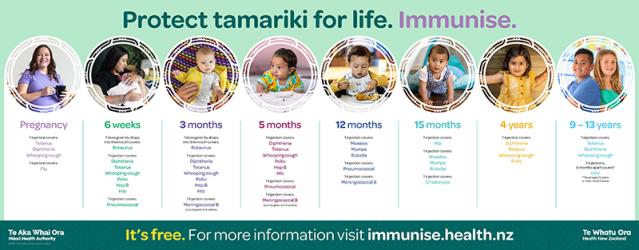

You can create a personalised immunisation schedule for your baby. By putting in your child's birthday, it will show you the immunisations your baby needs and when they should have them.
The chart below is just an example - create one for your child
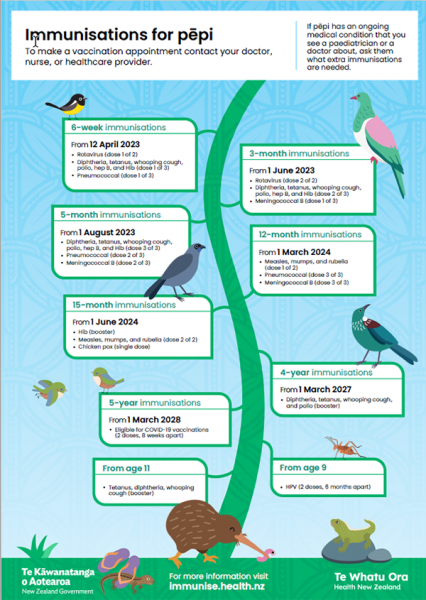
Some tamariki need extra immunisations:
- hepatitis B immunisation at birth - for all babies whose mothers have hepatitis B
- BCG immunisation to protect against tuberculosis
- meningococcal immunisation for those at increased risk of types A, C, Y and W
Talk to your GP practice.
Tips for when pēpi and tamariki have their immunisations
Immunisation Tips For Pēpi & Tamariki
After immunisation
Reactions to immunisation
Tamariki can have reactions to immunisations. Most of these are mild, such as redness on the arm or a grizzly child for a day or two.
A reaction is an expected sign that the immune response is building and the vaccine is working. Occasionally, more concerning reactions occur like prolonged crying. Although worrying at the time, research shows there are no long-term problems following such reactions. But, if you are concerned, contact your GP practice.
Paracetamol and immunisation
Tamariki are more likely to get a fever or a high fever after immunisation with MenB (Bexsero). When your pēpi has their MenB vaccine, paracetamol can help lower any fever and make them more comfortable.
Find out more about paracetamol and meningococcal immunisation.
Immunisation - your choice
Immunisation is not compulsory in New Zealand. There is a lot of inaccurate information on immunisation and this can be confusing. It's important to check out the source of the material. Ask:
- is it based on sound evidence?
- is it up to date information taking the latest research into consideration?
- does it relate to Aotearoa New Zealand?
Talk to your GP practice.
Watch a video from Immunise: Louis' parents talk about their anxiety around vaccine side effects
Video by Te Aka Whai Ora and Te Whatu Ora
More videos about immunisation
Watch a series of 10 short videos answering your questions about immunisation.
Immunisation Videos - Why Immunise?
Watch some short videos about protecting your child from serious disease.
Immunisation Videos - Protecting Your Child From Serious Diseases
Whānau talk about their experience of immunisation. Video by Auckland, Northland, Waitemata and Counties Manukau DHBs
